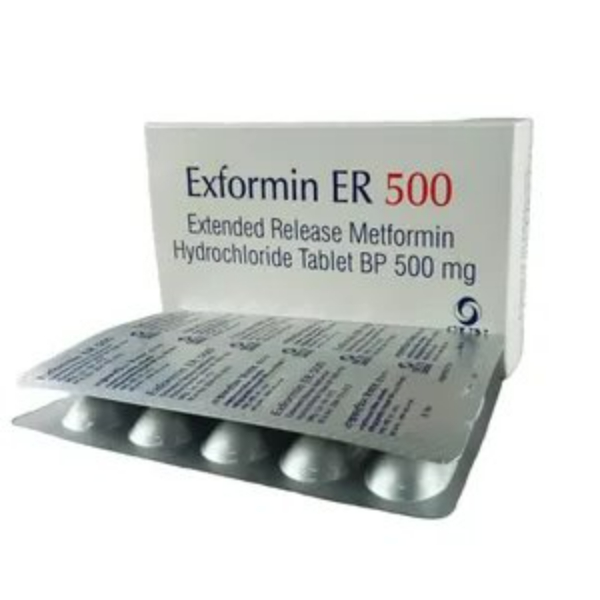
Description
• রেজিস্টার্ড চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন
🧾 Indications:
Management of type 2 diabetes mellitus, especially in overweight patients, when diet and exercise alone do not provide adequate glycemic control.
⚗️ Pharmacology:
Metformin works by reducing hepatic glucose production, decreasing intestinal absorption of glucose, and improving insulin sensitivity by increasing peripheral glucose uptake.
💊 Dosage:
Initial dose: 500 mg once daily with evening meal. Dosage can be adjusted based on patient response, up to a maximum of 2000 mg/day.
🩺 Administration:
Should be taken with food to reduce gastrointestinal side effects. Swallow whole, do not crush or chew.
🔄 Interaction:
May interact with alcohol, diuretics, corticosteroids, and other antidiabetic agents. Co-administration with iodine contrast agents may increase risk of lactic acidosis.
⛔ Contraindications:
Renal dysfunction, metabolic acidosis (including diabetic ketoacidosis), severe hepatic impairment, and hypersensitivity to Metformin.
⚠️ Side Effects:
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, metallic taste. Rarely, lactic acidosis may occur.
🤰 Pregnancy & Lactation:
Should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed and prescribed by a physician. Use with caution during lactation.
⚠️ Precautions & Warnings:
Monitor renal function regularly. Avoid alcohol. Stop treatment temporarily before surgery or use of contrast agents.
🧬 Therapeutic Class:
Biguanides (Oral hypoglycemics)
🧊 Storage Conditions:
Store in a cool and dry place, below 30°C. Protect from light and moisture. Keep out of reach of children.








.jpg)